Multi Tenant Analytics & Integration Platform
Jan 8, 2025

Project Type : Subcontract
Project Year : May 2024 - Feb 2025
Client Region: USA
Industry: IT Security
Context & Objectives
StackGenius partnered with a mid-sized US IT & Security company that managed multiple downstream tenants. The client was facing a critical challenge: their data sources—Okta, Intune, Jamf, Elasticsearch, and Jira/Atlassian—were siloed, making it difficult to get a unified view of tenant-level activity. Reporting was cumbersome, and each tenant required strict isolation while still maintaining a consistent user experience.
The goal of the project was to create a governed, multi-tenant lakehouse that unified all data sources while keeping tenant data isolated.
In Phase 1, the focus was on delivering a single, unified dashboard per tenant.
Phase 2 aimed to extend this with a front-end application featuring embedded analytics and a tenant-scoped API layer, orchestrating multi-source pipelines to enable seamless, self-service analytics.
Challenges
Before StackGenius, the client struggled with fragmented data sources and inconsistent analytics. Each system Okta, Intune, Jamf, Elasticsearch, and Jira/Atlassian had its own schema and access controls, making cross-tenant visibility difficult. Without a unified semantic layer, metrics and table joins were inconsistent, leading to conflicting results and manual reconciliation
Siloed Data Sources: Each system had its own schema and access model, making cross-tenant analytics difficult.
Inconsistent Metrics: Without a shared semantic layer, metrics and joins varied across teams.
Maintenance Overhead: Dashboard and query maintenance was tedious due to manual SQL or API integrations.
Scalability Issues: Adding new tenants or sources required substantial effort, creating high marginal costs.
Constraints & Non-Functional Requirements
The solution had to meet strict requirements around security, performance, reliability, and cost. Security and tenant isolation were non-negotiable:
Okta SSO handled authentication, while strong role- and attribute-based access controls (RLS/ABAC) ensured each user and service could only access the data they were authorized to.
Strict Security & Tenant Isolation: Leveraged Okta SSO, RLS/ABAC, and least-privilege service roles, with fully auditable dashboard embeds to ensure every tenant’s data remained secure and compliant.
Fast, Fresh, and Reliable Analytics: Operational views refreshed every 15 minutes, with dashboards designed to respond under 3 seconds.
Scalable and Cost-Efficient Platform: Engineered to scale from tens to hundreds of tenants without re-platforming, with budget alarms, tenant-aware caching, and right-sized compute/storage to optimize costs.
Solution & Implementation
To address the client’s challenges, we designed and implemented a multi-tenant Lakehouse solution with a phased approach.
In Phase 1, we unified siloed sources—Okta, Intune, JAMF, Elasticsearch, and Jira/Atlassian into a governed Lakehouse while maintaining strict tenant isolation.
Data was ingested via AWS Lambda and Step Functions, securely managed with KMS, and stored in S3 as raw and bronze layers. Databricks Delta Live Tables transformed the data into silver and gold layers, standardizing tenant keys and conforming core entities.
Dashboards were delivered through Power BI Embedded, giving each tenant a single, unified view of their data.
Phase 2 extended this with a custom front-end application and tenant-scoped APIs, enabling self-service analytics. Governance and security were enforced at every layer with Unity Catalog policies, RLS/ABAC, and audit logging.
Observability was ensured with CloudWatch, Delta audits, and reconciliation checks, while selective caching and partitioning by tenant and date optimized performance and cost.
Implementation Highlights
Ops: Automated DAGs for fetch → stage → validate → merge → reconcile → notify.
Security: Short-lived tokens via Okta, RLS/ABAC at semantic and embed-time, KMS-managed secrets, and embed request audit trails.
Quality: Data contracts enforced early; reconciliation across bronze, silver, and gold layers; domain rules like device existence before device state applied.
Performance Cost: Partitioned by tenant and date, bounded defaults for dashboard tiles, selective caching, and budget alarms with usage anomaly alerts.
Deliverables
The project delivered a complete, reusable analytics framework, including a registry of all data sources and their API details, fully configured DLT pipelines and jobs, Delta schemas with gold marts, a comprehensive RLS/ABAC policy pack with an embedding guide, and dashboards to monitor data freshness and reconciliation.
Source registry with API scopes and rate limits
DLT pipelines and job configurations
Delta schemas and gold marts catalog
RLS/ABAC policy pack and embedding runbook
Reconciliation dashboards and freshness monitors
Outcomes & Business Impact
The StackGenius solution delivered significant improvements across analytics, operations, and customer experience.
Time-to-insight was dramatically reduced tenant-level views that previously took weeks to generate could now be produced in days, allowing the client to make faster, data-driven decisions across authentication, devices, logs, and projects.
Operational uptime improved as unified observability helped the team detect and escalate incidents more quickly, reducing downtime and service disruptions.
From a customer perspective, tenants benefited from a simplified experience: one login and one dashboard per tenant streamlined access, lowered friction, and reduced support escalations. Additionally, the platform was designed for reuse and scalability.
Tech Stack
The StackGenius solution integrated multiple data sources, including Okta, Intune, Jamf, Elasticsearch, and Jira/Atlassian, accessed via APIs in JSON format.
Data ingestion was handled through AWS API Gateway and Lambda functions, with batched fetchers and KMS-managed secrets ensuring security and reliability.
The Lakehouse architecture leveraged S3 for raw and bronze storage, while Databricks Delta Lake managed silver and gold layers for structured, transformed data.
AWS Step Functions orchestrated end-to-end pipelines, including retries and dead-letter queues, ensuring robust and fault-tolerant operations.
Data transformation and modeling were handled with Databricks Delta Live Tables for silver data and Databricks Jobs/Workflows for gold marts.
For data consumption, Phase 1 dashboards were delivered through Power BI Embedded, and Phase 2 added a custom front-end with tenant-scoped APIs for interactive analytics.
Governance and security were enforced using Unity Catalog policies, Okta SSO, RLS/ABAC controls, and KMS-managed secrets, while observability and quality were ensured with CloudWatch logs, Delta audits, and reconciliation checks across all layers.
DevOps practices included Git-based Databricks code management, environment promotion, and infrastructure-as-code for pipeline deployment.
Finally, cost and FinOps controls such as budget alarms, usage telemetry, and tenancy-aware caching ensured the platform remained efficient and scalable.
Target Architecture
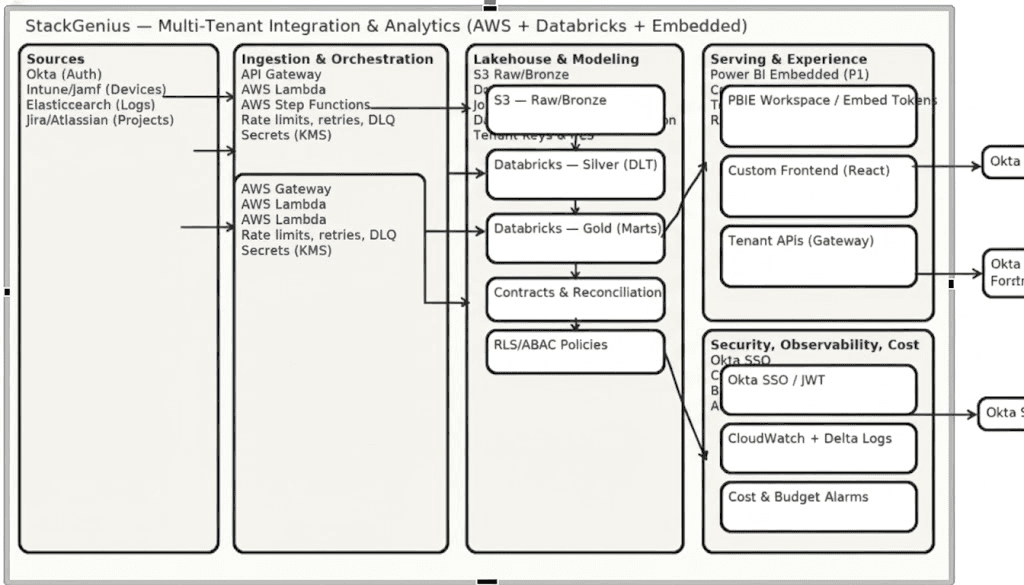
The StackGenius platform integrates multiple tenant data sources into a unified analytics and operational framework.
Data flows through five main layers:
Sources: Data is ingested from Okta (authentication), Intune/Jamf (devices), Elasticsearch (logs), and Jira/Atlassian (projects).
Ingestion & Orchestration: AWS API Gateway and Lambda functions handle data collection, while Step Functions manage orchestration and rate limiting.
Lakehouse & Modeling: Data is stored in S3 as raw and bronze layers, transformed into silver using Databricks Delta Live Tables (DLT), and further modeled into gold marts.
Serving & Experience: Phase 1 delivers dashboards via Power BI Embedded, while Phase 2 provides a custom React frontend and tenant-scoped APIs for interactive analytics, ensuring a seamless self-service experience for each tenant.
Security, Observability & Cost: Okta SSO/JWT tokens enforce authentication, CloudWatch and Delta logs monitor system health, and cost/budget alarms manage financial efficiency.
Data Model Highlights
The data model was designed to balance tenant-level isolation with enterprise-wide consistency. It introduces a structured semantic layer that ensures every tenant’s data remains secure, while enabling comparable, standardized analytics across sources.
Tenant-Scoped Keys
Every record is tied to tenant identifiers such astenant_id,org_id,source_system, andingest_at. These keys act as the foundation for row-level and attribute-based access control (RLS/ABAC), ensuring each tenant can only view their own data.Conformed Entities
To avoid siloed definitions, core business concepts were standardized into shared dimensions and facts:Dimensions:
dim_tenant,dim_user,dim_device,dim_projectprovide common reference points for identity, assets, and workstreams.Facts:
fact_auth_event,fact_device_state,fact_issuecapture detailed transactional data such as login attempts, endpoint compliance checks, and project workflows.
Core Measures
The model provides a set of go-to metrics that drive security and operational insight.MFA Adoption % : Tracks how widely tenants have rolled out multi-factor authentication.
Login Failure Rate : Monitors authentication risks and potential misconfigurations.
Endpoint Compliance % : Measures device adherence to security standards.
Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) : Quantifies responsiveness in addressing issues or incidents.
Backlog Burn : Tracks operational efficiency in reducing pending tickets or tasks.
Achieving a Single Source of Truth
With StackGenius, the client finally consolidated siloed data from systems like Okta, Intune, Jamf, Elasticsearch, and Jira into a governed lakehouse with full tenant isolation. This shift eliminated inconsistent definitions and manual dashboard maintenance, replacing them with a shared semantic layer and reusable gold marts. Beyond improving time-to-insight, this consistency has given the client confidence that their analytics are both secure and reliable a foundation they can scale on for years to come.